TechCrunch recently caught up with recent Y Combinator graduate Uiflow, a startup that is building a no-code enterprise app creation service.
If you are thinking wait, don’t a number of companies already do that?, the answer is yes. But what Quickbase, Smartsheet and others are working on isn’t quite the same thing, at least from the startup’s perspective.
Uiflow, a Bay Area-based concern that has been alive for far less than a year, has built an app creation tool that works with whatever backend a large company currently employs, and helps its development team build apps collaboratively. As the startup explained in a public posting, customer developers can import Figma files while their engineers can use existing UI libraries, and product managers can quickly vet an app’s logic.
The service is akin to a “cross between Unity and Figma,” Uiflow says.
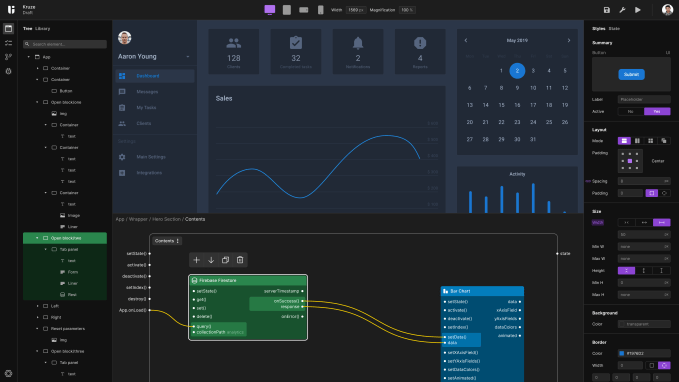
Here’s what its own user interface looks like, per a screenshot the company provided to TechCrunch after an interview:
Per Y Combinator, the company has closed a pre-seed round of more than $500,000. The company told TechCrunch that it has been talking to investors lately — as essentially every Y Combinator-backed startup does after their public unveiling — but appears to be holding off raising more capital until it fully launches self-service of its product; the company may also accelerate its hiring efforts once its self-serve GTM motion is more broadly available.
The startup told TechCrunch that after its Product Hunt launch it picked up around 1,200 signups. It’s vetting the group and letting in some as pilot customers. Those customers currently pay the company, so it has revenue, although the startup is more product-focused at the moment than centered around boosting its short-term revenues.
Uiflow thinks that its target customers are companies with 250 or more workers, the scale at which a company begins to start thinking about its own UI elements. However, Uiflow is talking to companies with 100 to 1,000 customers, it said.
The five-person team is building a service in a market that is more than active at the moment. As TechCrunch has explored, private-market investors are bullish on the no-code space, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic bolstered the pace at which companies large and small moved toward digital solutions. No-code and low-code services came into greater demand as accelerating digital transformation efforts met the market’s general dearth of available developer talent.
TechCrunch has covered the no-code space extensively in recent quarters, given both rising market demand for its products and what seemed to be growing investor demand for shares in startups pursuing the model. All that’s to say that there’s a reasonable chance that we’ll hear from Uiflow soon regarding a fresh capital raise. Let’s see how long that takes.
In the meantime, here’s a photo of the Uiflow team. In 2021-style, it’s a Zoom shot:

From upper left, clockwise: Michael Tildahl, Eric Rowell (CTO and co-founder), Brian Lichliter, Rocco Cataldo and D. Sol Eun (CEO and co-founder). Via the company.