In order to have innovative smart city applications, cities first need to build out the connected infrastructure, which can be a costly, lengthy, and politicized process. Third-parties are helping build infrastructure at no cost to cities by paying for projects entirely through advertising placements on the new equipment. I try to dig into the economics of ad-funded smart city projects to better understand what types of infrastructure can be built under an ad-funded model, the benefits the strategy provides to cities, and the non-obvious costs cities have to consider.
Consider this an ongoing discussion about Urban Tech, its intersection with regulation, issues of public service, and other complexities that people have full PHDs on. I’m just a bitter, born-and-bred New Yorker trying to figure out why I’ve been stuck in between subway stops for the last 15 minutes, so please reach out with your take on any of these thoughts: @Arman.Tabatabai@techcrunch.com.
Using ads to fund smart city infrastructure at no cost to cities
When we talk about “Smart Cities”, we tend to focus on these long-term utopian visions of perfectly clean, efficient, IoT-connected cities that adjust to our environment, our movements, and our every desire. Anyone who spent hours waiting for transit the last time the weather turned south can tell you that we’ve got a long way to go.
But before cities can have the snazzy applications that do things like adjust infrastructure based on real-time conditions, cities first need to build out the platform and technology-base that applications can be built on, as McKinsey’s Global Institute explained in an in-depth report released earlier this summer. This means building out the network of sensors, connected devices and infrastructure needed to track city data.
However, reaching the technological base needed for data gathering and smart communication means building out hard physical infrastructure, which can cost cities a ton and can take forever when dealing with politics and government processes.
Many cities are also dealing with well-documented infrastructure crises. And with limited budgets, local governments need to spend public funds on important things like roads, schools, healthcare and nonsensical sports stadiums which are pretty much never profitable for cities (I’m a huge fan of baseball but I’m not a fan of how we fund stadiums here in the states).
As city infrastructure has become increasingly tech-enabled and digitized, an interesting financing solution has opened up in which smart city infrastructure projects are built by third-parties at no cost to the city and are instead paid for entirely through digital advertising placed on the new infrastructure.
I know – the idea of a city built on ad-revenue brings back soul-sucking Orwellian images of corporate overlords and logo-paved streets straight out of Blade Runner or Wall-E. Luckily for us, based on our discussions with developers of ad-funded smart city projects, it seems clear that the economics of an ad-funded model only really work for certain types of hard infrastructure with specific attributes – meaning we may be spared from fire hydrants brought to us by Mountain Dew.
While many factors influence the viability of a project, smart infrastructure projects seem to need two attributes in particular for an ad-funded model to make sense. First, the infrastructure has to be something that citizens will engage – and engage a lot – with. You can’t throw a screen onto any object and expect that people will interact with it for more than 3 seconds or that brands will be willing to pay to throw their taglines on it. The infrastructure has to support effective advertising.
Second, the investment has to be cost-effective, meaning the infrastructure can only cost so much. A third-party that’s willing to build the infrastructure has to believe they have a realistic chance of generating enough ad-revenue to cover the costs of the projects, and likely an amount above that which could lead to a reasonable return. For example, it seems unlikely you’d find someone willing to build a new bridge, front all the costs, and try to fund it through ad-revenue.
When is ad-funding feasible? A case study on kiosks and LinkNYC

A LinkNYC kiosk enabling access to the internet in New York on Saturday, February 20, 2016. Over 7500 kiosks are to be installed replacing stand alone pay phone kiosks providing free wi-fi, internet access via a touch screen, phone charging and free phone calls. The system is to be supported by advertising running on the sides of the kiosks. ( Richard B. Levine) (Photo by Richard Levine/Corbis via Getty Images)
To get a better understanding of the types of smart city hardware that might actually make sense for an ad-funded model, we can look at the engagement levels and cost structures of smart kiosks, and in particular, the LinkNYC project. Smart kiosks – which provide free WiFi, connectivity and real-time services to citizens – have been leading examples of ad-funded smart city projects. Innovative companies like Intersection (developers of the LinkNYC project), SmartLink, IKE, Soofa, and others have been helping cities build out kiosk networks at little-to-no cost to local governments.
LinkNYC provides public access to much of its data on the New York City Open-Data website. Using some back-of-the-envelope math and a hefty number of assumptions, we can try to get to a very rough range of where cost and engagement metrics generally have to fall for an ad-funded model to make sense.
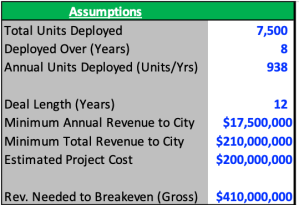
To try and retrace considerations for the developers’ investment decision, let’s first look at the terms of the deal signed with New York back in 2014. The agreement called for a 12-year franchise period, during which at least 7,500 Link kiosks would be deployed across the city in the first eight years at an expected project cost of more than $200 million. As part of its solicitation, the city also required the developers to pay the greater of either a minimum annual payment of at least $17.5 million or 50 percent of gross revenues.
Let’s start with the cost side – based on an estimated project cost of around $200 million for at least 7,500 Links, we can get to an estimated cost per unit of $25,000 – $30,000. It’s important to note that this only accounts for the install costs, as we don’t have data around the other cost buckets that the developers would also be on the hook for, such as maintenance, utility and financing costs.
Source: LinkNYC, NYC.gov, NYCOpenData
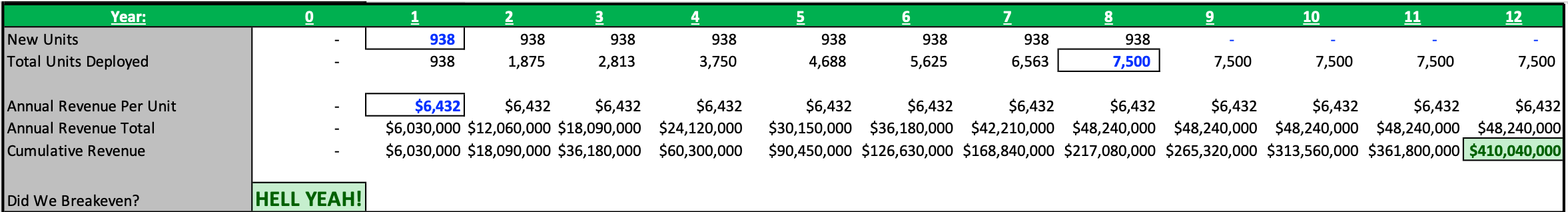
Turning to engagement and ad-revenue – let’s assume that the developers signed the deal with the expectations that they could at least breakeven – covering the install costs of the project and minimum payments to the city. And for simplicity, let’s assume that the 7,500 links were going to be deployed at a steady pace of 937-938 units per year (though in actuality the install cadence has been different). In order for the project to breakeven over the 12-year deal period, developers would have to believe each kiosk could generate around $6,400 in annual ad-revenue (undiscounted).
Source: LinkNYC, NYC.gov, NYCOpenData
The reason the kiosks can generate this revenue (and in reality a lot more) is because they have significant engagement from users. There are currently around 1,750 Links currently deployed across New York. As of November 18th, LinkNYC had over 720,000 weekly subscribers or around 410 weekly subscribers per Link. The kiosks also saw an average of 18 million sessions per week, or 20-25 weekly sessions per subscriber, or around 10,200 weekly sessions per kiosk (seasonality might even make this estimate too low).
And when citizens do use the kiosks, they use it for a long time! The average session for each Link unit was four minutes and six seconds. The level of engagement makes sense since city-dwellers use these kiosks in time or attention-intensive ways, such making phone calls, getting directions, finding information about the city, or charging their phones.
The analysis here isn’t perfect, but now we at least have a (very) rough idea of how much smart kiosks cost, how much engagement they see, and the amount of ad-revenue developers would have to believe they could realize at each unit in order to ultimately move forward with deployment. We can use these metrics to help identify what types of infrastructure have similar profiles and where an ad-funded project may make sense.
Bus stations, for example, may cost about $10,000 – $15,000, which is in a similar cost range as smart kiosks. According to the MTA, the NYC bus system sees over 11.2 million riders per week or nearly 700 riders per station per week. Rider wait times can often be five-to-ten minutes in length if not longer. Not to mention bus stations already have experience utilizing advertising to a certain degree. Projects like bike-share docking stations and EV charging stations also seem to fit similar cost profiles while having high engagement.
And interactions with these types of infrastructure are ones where users may be more receptive to ads, such as an EV charging station where someone is both physically engaging with the equipment and idly looking to kill up sometimes up to 30 minutes of time as they charge up. As a result, more companies are using advertising models to fund projects that fit this mold, like Volta, who uses advertising to offer charging stations free to citizens.
The benefits of ad-funding come with tradeoffs for cities
When it makes sense for cities and third-party developers, advertising-funded smart city infrastructure projects can unlock a tremendous amount of value for a city. The benefits are clear – cities pay nothing, citizens are offered free connectivity and real-time information on local conditions, and smart infrastructure is built and can possibly be used for other smart city applications down the road, such as using locational data tracking to improve city zoning and congestion.
Yes, ads are usually annoying – but maybe understanding that advertising models only work for specific types of smart city projects may help quell fears that future cities will be covered inch-to-inch in mascots. And ads on projects like LinkNYC promote local businesses and can tap into idiosyncratic conditions and preferences of regional communities – LinkNYC previously used real-time local transit data to display beer ads to subway riders that were facing heavy delays and were probably in need of a drink.
Like everyone’s family photos from Thanksgiving, the picture here is not all roses, however, and there are a lot of deep-rooted issues that exist under the surface. Third-party developed, advertising-funded infrastructure comes with externalities and less obvious costs that have been fairly criticized and debated at length.
When infrastructure funding is derived from advertising, concerns arise over whether services will be provided equitably across communities. Many fear that low-income or less-trafficked communities that generate less advertising demand could end up having poor infrastructure and maintenance.
Even bigger points of contention as of late have been issues around data consent and treatment. I won’t go into much detail on the issue since it’s incredibly complex and warrants its own lengthy dissertation (and many have already been written).
But some of the major uncertainties and questions cities are trying to answer include: If third-parties pay for, manage and operate smart city projects, who should own data on citizens’ living behavior? How will citizens give consent to provide data when tracking systems are built into the environment around them? How can the data be used? How granular can the data get? How can we assure citizens’ information is secure, especially given the spotty track records some of the major backers of smart city projects have when it comes to keeping our data safe?
The issue of data treatment is one that no one has really figured out yet and many developers are doing their best to work with cities and users to find a reasonable solution. For example, LinkNYC is currently limited by the city in the types of data they can collect. Outside of email addresses, LinkNYC doesn’t ask for or collect personal information and doesn’t sell or share personal data without a court order. The project owners also make much of its collected data publicly accessible online and through annually published transparency reports. As Intersection has deployed similar smart kiosks across new cities, the company has been willing to work through slower launches and pilot programs to create more comfortable policies for local governments.
But consequential decisions related to third-party owned smart infrastructure are only going to become more frequent as cities become increasingly digitized and connected. By having third-parties pay for projects through advertising revenue or otherwise, city budgets can be focused on other vital public services while still building the efficient, adaptive and innovative infrastructure that can help solve some of the largest problems facing civil society. But if that means giving up full control of city infrastructure and information, cities and citizens have to consider whether the benefits are worth the tradeoffs that could come with them. There is a clear price to pay here, even when someone else is footing the bill.
And lastly, some reading while in transit:
- How California’s Efforts to Prevent Wildfires Reflect a National Crisis on Climate Change – The New Yorker, Carolyn Kormann
- A’s Propose Crazy-Looking Howard Terminal Stadium, Financial Details Still Uncertain – Field of Schemes, Neil deMause
- Berlin’s Massive Housing Push Sparks a Debate About the City’s Future – CityLab, Feargus O’Sullivan
- Magnetic Levitation: The Return of Transport’s Great ‘What If?’ – The Guardian, Christopher Beanland
- Addis Ababa Has Overtaken Dubai as the World’s Gateway into Africa – Quartz, Abdi Latif Dahir
- Planning a Neighborhood Square – The Western Planner, Dr. Suzanne H. Crowhurst Lennard

No comments:
Post a Comment